|
Researchers: Hong Li, Ph.D. student, Prof. Lorne Mason & Prof. Michael Rabbat
Description:
Problem: To provide better service to VoIP customers, overlay networks
have been employed to route voice packets. Much recent
research has focused on VoIP QoS routing in overlay networks.
However, the pair of paths are usually either
selected arbitrarily or via brute-force search. No previous work
has considered how two or more paths can be selected to
maximize VoIP quality in a distributed and scalable fashion.
In this work, we demonstrate improved VoIP quality in a
distributed and scalable fashion.
When a link on the primary or the secondary optimal path
fails, all the voice calls on it will be dropped. It is important
to be able to detect the link failure as early as possible.
The primary and the secondary optimal next hop learning algorithms
are able to detect a link failure
after the probability of choosing the failed link drops to be
smaller than that of other choices.
Approach: By using a learning automaton (a form of
reinforcement learning agent), we quickly learn which paths
have little potential to provide sufficient quality of service
for a given destination.
Such probing and learning is implemented
for both the primary and the secondary optimal next
hop learning automata. A link failure detection approach based on the change of learning automata parameters is
also proposed.
Simulation Results:
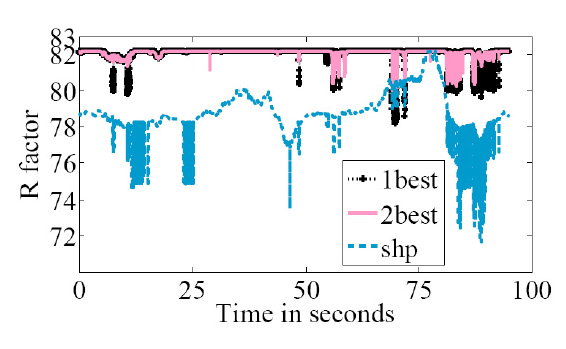
Fig: Average R-factor for all source-destination pairs. The dashed line
shows the average R-factor for shortest hop path routing (shp). The two lines
above the dashed line are the average R-factor for "1best" routing and that
for "2best" routing, which overlap each other most of the time. However,
the R-factor for "2best" routing is slightly better and more stable than that
for "1best" routing. With "2best" or "1best" routing method, voice quality is
improved from "medium" to "high" level. the average R-factor for "1best"
routing is mostly above 80 (at high quality level); the average R-factor for
"2best" routing is always above 80 and close to 82.2 (which is the maximum
R-factor for G.729 codec).
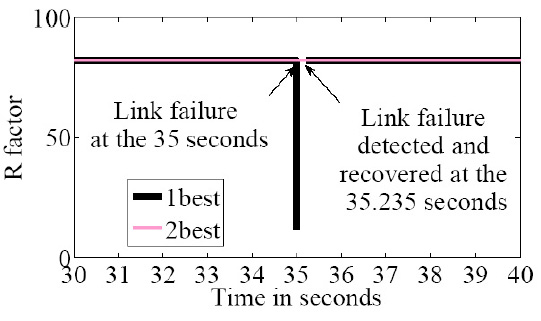
Fig: R-factor comparison for a single source-destination pair when link
failure detection is implemented. The thick solid line shows the R-factor for the ”1best” routing. The
dashed line shows the R-factor for the ”2best” routing.
Publications:
H. Li, L. Mason and M. Rabbat, "Learning Optimal Diverse Paths for Voice-Over-IP in Service Overlay Networks: a Distributed, Scalable and
Robust Solution", submitted to IEEE Trans. Network and Service Management.
|



